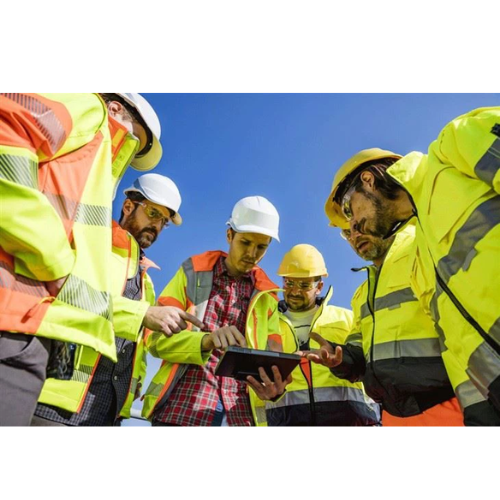
Your Professional Reflective Clothing Supplier
What is reflective clothing?
The purpose of reflective clothing, also known as high-visibility warning clothing, is to signal the presence of the user in places and situations which may cause potential threats to their health and safety. Such signalling must be effective at any time of day and night, when it is dark – in the light of vehicle lamps, headlamps as well as street lighting, e.g. on municipal roads. Reflective clothing is commonly used by construction workers and those performing maintenance works on motorways and roads or tracks e.g. railway tracks, airports, docks and wharfs. It should also be used wherever there is risk that a worker may collide with or be hit by moving machines or objects.
Advantages of Reflective Clothing
The reflective material of a reflective clothing is crucial, and has a variety of reflective materials to meet the needs of various scenarios,including TC Premium Silver Tapes,3M 89D6,Hi Vis Contrasting Tapes ,Reflective PVC Tapes etc…
Reflective clothing has the following regular seven types of fabrics:(1)Polyester Soild(2)Polyester Mesh(3)Birdeye Polyester(4)Poly/Cotton(5)Oxford Polyester(6)Fleece Polyester(7)FR Treated(8)Cold Absorbent Material
And some specially fabrics as following:(1)Polypropylene.Polyester(2)Polyester With Spandex(3)Bamboo/Polyester
TECHNICAL DETAILS
Full front zipper, elasticized waist and cuffsward off wind and snow.
Sealing strip can keep out water.
Stretch and reinforced panels allow ease ofmovement with added durability.
Advantages of Reflective Clothing
The company spends more than $10 million a year on research and development, and has more than 28 designers and researchers to help customers develop new products, so if you want to customize the logo, we can meet you!
They was set up extremely based on factory audit standard and now already passed
several standards.
Products Certification
As an international high visibility garments manufacturer, our products satisfy different countries standard. Some products have CE certification that recognized by third profession a groups.In addition, raw materials and cloths have SGS/SATRA testing reports
Reflective Clothing For Professional Use – Requirements
In order to fulfil its essential function, i.e. signal the presence of the user both during the day and night, reflective clothing should be made from two kinds of high-visibility materials: the background material with fluorescent properties, which ensures visibility during the day, as well as retro reflective material or combined-performance material. The retroreflective and combined-performance materials reflect the light back to its source and, thus, ensure that in the darkness the clothing is visible in the light of the vehicles.
According to EN ISO 20471 reflecting clothing is grouped into three classes. Each class has minimum areas of high-visibility materials incorporated in the garment in accordance with Table 1.
| Class 3 garments | Class 2 garments | Class 1 garments | |
| Background material | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.14 |
| Retroreflective material | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.1 |
Source: EN ISO 20471[2]
To ensure visibility from all sides (360° visibility), it is important that horizontal retro reflective bands and fluorescent materials encircle torso, trouser legs and sleeves. All class 3 garments must cover the torso and have as a minimum either sleeves with retroreflective bands or full length trouser legs with retroreflective bands.
Class 3 reflecting clothing is characterised by having greater conspicuity in most types of urban and rural surroundings than class 2, which at the same time is significantly more conspicuous than class 1.
Materials Used In Reflective Clothing For Professional Use
Fluorescent background material

In order to ensure visibility of a worker throughout the entire cycle of use of the reflective clothing, the background material which complies with the EN ISO 471 should retain the colour in a specified period of time, even if the clothing is exposed to sunlight, changeable weather and maintenance cycles. This is why the chromaticity coordinates of the background material colour should fulfil the requirements after an indicated cycle of exposure to xenon light. After the test, the colour should still meet the requirements indicated in EN ISO 20471. The colour of the material of the reflective clothing should also be resistant to a number of maintenance cycles (laundry or dry-cleaning) indicated by the manufacturer of the clothing and also to rubbing by another material. Reflective clothing – besides fluorescent background material – may also be composed of non-fluorescent material in any colour (e.g. navy), in proportions appropriate for the given class of clothing. The EN ISO 20471 standard states, however, that the material should be characterised by good colour fastness in particular with respect to laundry and rubbing, which will ensure protection of the fluorescent background material colour (e.g. orange-red) during the usage of the clothing.
Retroreflective material
The essential quality characteristic of retroreflective materials is the coefficient of retroreflection. In order to ensure a proper level of protection during use, the retroreflective material in compliance with the EN ISO 20471 standard should meet the requirements relating to the coefficient of retroreflection even after cycles of maintenance, abrasion, flexing, folding at cold and influence of rainfall. These kinds of tests are most often performed in the process of certification of the retroreflective material in relation to compliance with the EN ISO 20471 standard.
Combined-performance material
The so-called combined-performance materials meet the requirements specified both for the background materials (visible during the day) and retroreflective materials (ensuring visibility during the night). They are characterised by much higher effectiveness and ensure better visibility of the worker.
Performance tests
The minimum requirements given under the EN ISO 20471 standard are determined by the specific test methods and their assigned measuring values. The tests are partly performed on new materials and partly on preconditioned materials. However, it should be noted that laboratory testing may not represent real life conditions. Even if performance of materials is determined after simulating real life conditions (e.g. exposure to Xenon light or washing cycles) there has not been any known relationship yet between the materials’ performance and wear time or actual realistic conditions of wear. The conspicuity performance of a garment will depend on usage (e.g. dirt, solar irradiation), care (e.g. cleaning agent, repair), storage (e.g. dust-free, lightproof), etc., so wear of the clothing during use should be observed.